This blog focuses on how to leverage the knowledge held, created, shared in an organisational context; with the objective of fostering creativity and innovation for competitive advantage. Leveraging your organisational knowledge relates to Knowledge Management, organisational learning, human capital development, social media/networks strategy, multi-channels Customer Relationships Management (CRM)
Search This Blog
29 August 2006
What if we tried to foresee what will follow the currently unfolding Knowledge Economy?
What if we tried to foresee what will follow the currently unfolding Knowledge Economy? What will be the new buzz word for corporate leaders in 2050?I will not attempt here to answer these questions directly but will use scientific predictions as metaphors to give us a hint.
While reading recently the very interesting scientific book “The Next Fifty Years – Science in The First Half of the Twenty-First Century”, a collection of 25 new essays by leading scientists edited by J. Brockman (A Vintage Original, New-York, 2002) I found three passages from three different authors that are relevant to my two questions above.
First, here is how Alison Gopnik (professor of psychology at the University of California at Berkeley) ends her essay “What Children Will Teach Scientists”:
“[…] At the end of the last century, knowledge began to become the most valuable currency, like land in a feudal economy or capital in an industrial economy. The new science of learning should tell us that knowledge is not just a prize to be won in some desperate test-taking struggle for places in the contemporary mandarinate. Instead it is, literally and not just rhetorically, our universal human birthright.”
The way I read this (based also on the reading of Alison’s whole essay about the science to understand learning) is that our societies will progressively realise that knowledge is what makes us, humans, so special. The value of knowledge would then take the forefront in all aspects of our everyday life. We would continuously seek better ways to acquire it, to retain it, to share it, to nurture it. Of course, this should have a profound impact on management and organizational cultures. By 2050, the fact that knowledge is a vital asset will be a given fact and competitive advantage will be won by those who will leverage it faster and more effectively. This should mean that organizations of this future will have as a constant priority to make all their collaborators as creative and innovative as possible. Everyone in an organization will be empowered and encouraged to create/innovate making some mistakes along the way but learning a great deal more. This seems to be compatible with the next extract below.
Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi - a Hungarian-born polymath, formerly chairman of the Psychology Department at the University of Chicago and currently Davidson Professor of Management at the Claremont Graduate University in Claremont, California – writes in his essay “The Future of Happiness”:
“[…] Among the things we learned is that people who are engaged in challenging activities with clear goals tend to be happiest than those who lead relaxing, pleasurable lives. The less one works just for oneself, the larger the scope of one’s relationships and commitments, the happier a person is likely to be. […]”
Mihaly sees that by 2050, societies at large but employers in particular will have understood that people are more productive when they are happier, and that people are happier if they have challenging objectives and if these objectives are clearly contributing to the corporate goals. This seem to suppose that individuals will be valued for their specific knowledge and competencies to go beyond what is initially expected of them, in order to create value for the organization.
This nicely leads us to the third extract of this book I believe relevant to the leveraging of Knowledge. I found it at the end of Brian Goodwin’s essay titled “In The Shadow of Culture” where he attempts to explain why he believes a “science of qualities” is developing, where feelings and qualities have at least as much importance as proofs and quantities. Brian (a professor of biology at Schumacher College, Darlington, UK - where he coordinates a master’s program in holistic science- and a member of the Santa Fe Institute) writes:
“[…] In the shadow of current science it is possible to see the components of a science of qualities which would restore qualitative evaluation to the place it occupies in our everyday lives, where judgments depend on quality as well as quantity. This restoration, together with the recognition that feelings belong not only to us but also to the rest of nature, in whatever form, presents us with a dramatically transformed set of possibilities for scientific knowledge, technology, and corporate and political action.
A shift in scientific perspective of this magnitude is not going to happen overnight, if it happens at all. It requires new forms of education at a basic level, in which the sciences and the arts are united to keep people whole and in which scientific and technological decision-making require participation by all members of civil society, with knowledge joined again to responsible action.”
This extract is heavy in meanings and could open up many philosophical debates. I will only say this: if science does indeed go through such a drastic shift towards valuing qualitative judgment, it will have an even bigger impact on other parts of society such as the business world. Accounting would no longer rely on quantitative analysis and the value of a company would give at least as much importance to qualitative aspects such as its intellectual property, including the specific knowledge of all its collaborators.
Peter-Anthony Glick
http://leveragingknowledge.blogspot.com
22 June 2006
Traditional strategies to improve efficiency are failing in the Knowledge Economy.
It is really amazing and sad (and frustrating for some of us who can see the light) how much Company Boards concerned with cutting costs while sustaining growth can repetitively miss the most effective way to do this in the Knowledge Economy we leave in: leveraging the organizational Knowledge through the development of a knowledge-sharing culture to foster creativity and innovation.
Traditional means of cost cutting are increasingly reaching their limits and sometimes even become counter-productive. For instance, the still somewhat popular engineering tools designed to map, understand and control organizational processes – to eventually simplify/standardise them to cut costs and improve efficiency - are all failing to meet their objectives. They at best provide a partial understanding of what is really going on, and at worse end up being themselves more complex and costly to manage than what they are supposed to represent. The key problem of these tools is that they miss a vital part of organizational processes: the human aspects (social, political, hierarchical, geographical, knowledge, skills, competences, etc…).
Another example of a management tool usually not adapted to the Knowledge Economy is MBO or Management By Objectives. When managers’ performance is evaluated solely on annual objectives, they will naturally tend to focus their attention and efforts on these objectives and not be concerned with anyone else’s. In other words, MBO can have adverse effects on collaboration. Of course, there are ways to alleviate this problem such as including a knowledge-related objective for each manager. Assuming it is measurable, this objective would however probably drive the only knowledge-related activity a manager will carry out effectively, so not vey productive from a KM point of view.
Cost-cutting is still too often synonymous of redundancies, recruitment freeze, modest salary increase, low (or no) bonuses, etc… Of course, who is making the most sacrifices and suffers the most: the workforce (the human capital). The problem with this is that it affects negatively what is increasingly the most important asset to an organization: its people knowledge and experience. Instead of sending the message that their very existence is a reason for lower margins, they should be asked and given the suitable environment to actively and creatively work out ways to cut costs and/or increase efficiency/effectiveness with same resources. A suitable environment means enabling a knowledge sharing culture.
Peter-Anthony Glick
http://leveragingknowledge.blogspot.com
Labels:
collaboration,
innovation,
KM,
People/Culture,
Strategy
02 June 2006
Business Intelligence for simulating the future
Chris Caren (Microsoft’s general manager of Office business applications) had recently this to say about Business Intelligence:
The latest three trends are:
1. BI products are usually considered as too hard for everyone to use and too expensive to roll out to as many people as one would want to.
2. Standardising onto one or two BI product lines that can serve all the needs of different types of user.
3. A change in the way people are thinking about BI: from a report-centric, historical view of the business, to a metrics-centric view – involving dash-boards and scorecards – of where the company is heading.
I believe these three points are all valid and important but the last one is the key to success. The first two are more about technology, the last one is first about a change of approach and a change of objectives. It implies the realization that successful organizations will be the ones that focus on simulating the possible future rather than analysing the past.
Peter-Anthony Glick
http://leveragingknowledge.blogspot.com
18 May 2006
Seven lessons learned with Knowledge Management initiatives
If a shared information repository contains mostly information that people are used to find elsewhere, you’re wasting your time, it won’t be used.
“[...] make sure the system is easy and comfortable to use – in fact, easier and more comfortable than ignoring the system.” R. Buckman
For an individual (or a group) to contribute information, he/she must expect and obtain at least as much in return.
A deep cultural change in the organization can only succeed with a top-down approach.
Start small with “quick wins” and build on their growing reputation.
Pilot each new solution with welcoming teams and individuals. Keep the most resistant groups for last, they’ll follow when every one else is on board.
The “correct” level of information categorization depends on the tool, on the purpose and on the intended user community: Too much categorization adds unnecessary complexity and stifles creativity; too little leads to unproductive chaos.
Peter-Anthony Glick
http://leveragingknowledge.blogspot.com
03 April 2006
Systems thinking for Knowledge Management
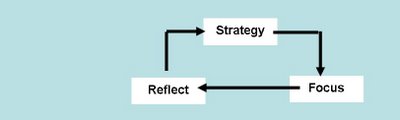 Consider the above “Strategic Capability” diagram (L. Baird and J. Henderson, The Knowledge Engine, Berrett-Koehler Publishers, 2001, first edition page 14).
Consider the above “Strategic Capability” diagram (L. Baird and J. Henderson, The Knowledge Engine, Berrett-Koehler Publishers, 2001, first edition page 14).
Business Intelligence (BI) needs to provide the right Knowledge to drive the strategy and use the strategy to direct Knowledge Management (KM) initiatives:
The Focus stage above.
The BI Reflect stage must rely heavily on Knowledge generated at the operational level (this same Knowledge is considered as “only” Information at the Strategic Level). Reflecting is about aggregating and simplifying this “operational Knowledge”, making sense of it strategically to produce “strategic Knowledge”.
“Making sense of Information” means here to be able to use it in various pre-defined contexts and run simulations. These simulations are to assist the strategic decision-makers in assessing which strategies have the most suitable potential-to-risk ratio.
How should the operational Knowledge be structured to enable these strategic simulations?
I have been recently introduced by Dennis Sherwood (author of “Seeing the Forest for the Trees – A Manager’s Guide to Systems Thinking”, Nicholas Brealy Publishing, 2002) to Systems Thinking in the organizational context. I strongly recommend Dennis’ book but in a few words, “the essence Systems Thinking is that the complexity of the real world can best be tamed by seeing things in the round, as a whole. […] Taking a broad view, however, is not at the expense of missing the detail […]. Nor is it a question of broad brush versus detail; rather, it is one of taking a broad view in the context of the right detail, of truly […] seeing the forest for the trees.”
The idea here is then to illustrate operational Knowledge in a systemic form (a causal loop more precisely) where all stakeholders are linked up through a network of inputs and outputs. These ins and outs are to represent the influences these stakeholders have on each other. Influences are either positive or negative (never neutral).
These systems include levers and outcomes. The levers are the variables for defining an initial context for the simulation. The outcomes give the results of the simulation.
Various off-the-shelves software will enable you to relatively easily design such an organizational system.
However, the complexity isn’t with the technical design but rather with defining the relationships between stakeholders, or in other words, with having a clear understanding of how the organization operates.
Building effective organizational systems must therefore involve experienced individuals from different key functional areas in the organization. No single individual can have the required knowledge to do this alone.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)